
Take a minute to think about all the ways your phone impacts your day. When you have a question, you Google it. If you don’t have cash for your coffee, you pay for it with an app. Whenever you want news, you can get it in any number of ways, even on a browser. Mobile internet doesn’t just improve your life — it’s an integral part of it.
In 2018, nearly 300 million consumers gained access to mobile internet for the first time. For many people in developing countries, mobile is their only option because in-home broadband is cost-prohibitive. The following chart shows fixed broadband prices as a percentage of Gross National Income (GNI). Compared with developed countries, the amount of income that would need to be allocated to broadband internet is significantly higher.
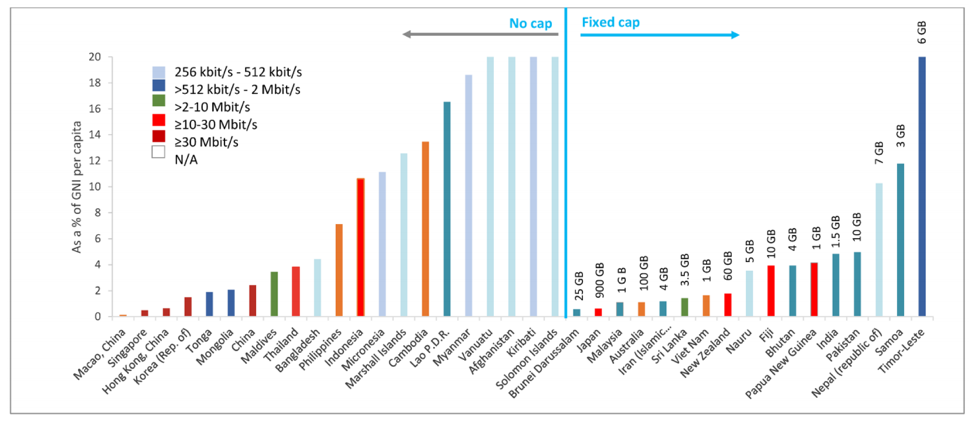
For people in developing countries, the benefits of mobile internet go far beyond convenience. It is their gateway to a world of information. When these people get connected, they can take charge of their finances, stay up to date with news, manage their health, find career opportunities, improve their education, and so much more. Mobile internet can change their lives for the better.
Mobile internet keeps people more informed
When developing countries get connected, they gain access to information related to health care, professional development, and news.
Health information and services
Not only does the internet offer a wealth of information that helps people stay more informed about their personal health, it also provides a way for them to connect with nearby clinics and doctors.
In South Africa, nurses and doctors use mobile internet to empower their patients. Thanks to the Mobile Health Information System, doctors and nurses have access to lifesaving information about infectious diseases, such as tuberculosis, malaria, HIV/AIDS, diarrhea, and pneumonia. Patients with mobile internet access can be given digitized treatment information so that they can care for themselves once they leave the clinic.
Health care professionals in South Africa also depend on mobile internet to provide accurate diagnoses, prescribe proper treatments, and supply the correct dosages of medicine. In some cases, mobile connectivity can save lives.
For example, Sierra Leone has begun testing a wearable Ebola sensor that monitors vital signs remotely. The device allows health care professionals to monitor patients and catch warning signs early, while also protecting themselves from exposure to Ebola.
Career opportunities
Connected people have the ability to significantly improve their career prospects. According to Intel’s Women and the Web study of low- and middle-income countries (LMICs), 59% of women in India and 47% of women in Uganda have used the internet to search for jobs. As a result, they’ve been able to learn about job opportunities outside of their immediate communities. This provides businesses with more applicants, and workers with better access to paid work.
Mobile internet also provides new income and professional networking opportunities. Nearly 40% of female internet users in Mexico and Egypt and 60% in Uganda reported that internet access helped them expand their networks. Plus, over 30% of women in India, Mexico, and Uganda were able to earn additional income online.
Local news
Access to local news and information allows consumers to stay informed about politics, weather, and their community. Without mobile internet, many people in emerging markets would not have a way to get any news, much less news specific to their area.
Companies like Hivisasa are already catering to the mobile market. Their mission is to provide news and information to populations in Africa. The crowd-sourced news site depends on “citizen reporters,” who submit stories through mobile phones. Once their story is accepted, citizen reporters can receive digital payments through the popular mobile payment app, M-Pesa.
Free Basics by Facebook also aims to make information more accessible to consumers using mobile internet connections. However, they take it a step further by making that access affordable as well. To do this, Free Basics simplifies informational websites so that they can be accessed without the user incurring any data charges. Because the high cost of data in some areas can cause many consumers to limit their mobile phone use, data-free websites are extremely beneficial.
Mobile internet makes education accessible
Internet access opens up a variety of valuable resources to both teachers and students. While teachers are able to better research and plan their curriculums, students can engage with the material through educational games and deeper investigation.

These benefits are particularly impactful in low-income areas. According to a study that included several low-income schools, test scores rose 30% after students were given mobile internet access. Similarly, a study including three schools, two of which are in Africa, showed that test scores rose significantly when students were given access to literacy apps.
Clearly, educational mobile apps have the potential to make a difference in the lives of school children around the world.
The Play ‘n’ Learn initiative in India is a great example. The program features educational content from India’s version of Sesame Street (Galli Galli Sim Sim) and revealed that school children ages 6-8
- made greater improvements in language comprehension, vocabulary, and imagination compared to students who did not have access to the content;
- strengthened their digital literacy skills by learning how to operate the camera and make calls on mobile devices;
- showed increased engagement with math and Hindi lessons; and
- improved their school attendance.
Lastly, mobile internet access encourages learning outside of the classroom. Surveys in Egypt, India, Mexico, and Uganda suggest that 77-84% of females use the internet to do further research with many claiming that this leads to higher grades.
Mobile internet promotes financial inclusion
Worldwide, approximately 1.7 billion people do not have access to reliable financial services. Not only does this leave them without banking services, but it also prevents them from learning how to save money and plan for the future. Mobile internet access contributes to greater financial inclusion by facilitating financial education and mobile money options.
Due to the lack of financial services, many countries still rely heavily on cash, which can be risky. In Sub-Saharan Africa, for example, cash is often sent via bus, with traveling friends, or carried over long distances, which puts people at risk of being robbed in transit.
Mobile payment options provide a safe and convenient alternative. In Kenya, mobile money has expanded from cash transfer services to avenues for paying utility bills and paying for goods and services at many businesses. Paying via mobile eliminates both the risk of carrying cash and the additional costs of transporting it.
Furthermore, mobile internet encourages financial education and income planning:
- 54% of female respondents to ONE’s Making the Connection survey have used mobile devices to look up information on financial services and banking.
- Farmers in Kenya use mobile internet to manage their supply chains, which has led to an average 13% increase in their income.
- Cocoa farmers in Ghana use mobile money to connect with agribusinesses, which allows them to receive payments regularly, run reports, and create budgets.
With mobile internet, populations are able to learn how to manage their money and have safe ways to send and receive payments.
Mobile internet boosts economies
With increased financial inclusion comes a more educated population that facilitates economic growth. Once people have the ability to make purchases, start businesses, and manage their finances, the entire economy benefits. In fact, the GSMA State of Mobile Internet Connectivity report revealed that “a 10% increase in mobile broadband penetration yields a 1.8% increase in GDP in middle-income countries and a 2% increase in low-income countries.”
Although mobile internet contributes to economic boosts in many ways, job creation is one of the most significant impacts. A study of 13 countries estimates that mobile internet led to the creation of 3 million jobs, many of which stayed in the surveyed countries. Naturally, the demand for mobile phones leads to jobs in manufacturing the devices as well as in retail, where the phones are sold.
Of course, the career opportunities don’t stop there. Newly connected consumers want apps that allow them to make the most of their mobile phones. As such, developers around the world have the chance to design and monetize apps for these emerging markets. Moreover, larger-scale operations, such as the booming mobile money industry, have the potential to create thousands of jobs. Uganda, for instance, has already created 200,000 jobs as a direct result of the demand for mobile money solutions.
Mobile internet empowers women
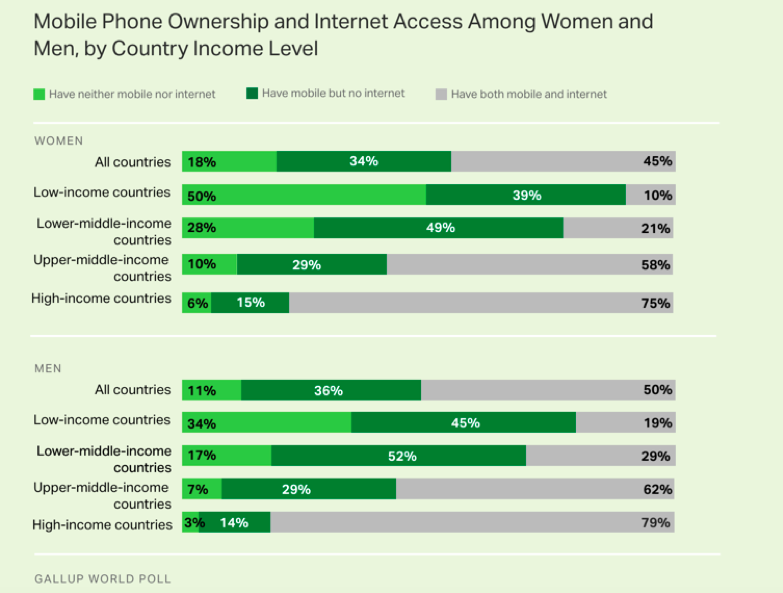
Globally, there is a significant mobile gender gap. In low-income countries, up to 50% of women have no access to the internet compared to 34% of men who remain unconnected. While mobile internet can improve the lives of men and women alike, the benefits of getting more women online are far-reaching.
Firstly, closing the mobile gender gap further boosts the economy. If as many women as men could gain mobile internet access in low-income countries, the GDP would see a $700 billion increase.
Connected women also contribute by entering the workforce and starting online businesses. In Malaysia, female entrepreneurship has greatly benefitted from a program that relies on mobile internet access to connect aspiring businesswomen with experienced mentors around the world.
Likewise, young girls make notable contributions when they get connected. Over 15,000 females access Intel’s She Will Connect coding training online. As a result of this program, a group of schoolgirls in Kenya worked together to create a mobile app that connects organ donors to patients as well as to hospitals that can perform the transplants.
Perhaps the most empowering aspect of women getting online is the many ways it improves their autonomy by
- allowing them to expand their communities;
- giving them a way to voice opinions online and engage in global conversations;
- exposing them to new ideas and information outside of their local communities;
- preventing them from being isolated or missing out on opportunities when communications and businesses move online; and
- providing opportunities for them to manage their own finances.
Mobile internet is a powerful resource
Mobile internet certainly makes lives easier, but for people in emerging markets, it can be truly life-changing. Next time you head to Google for a trivia answer, think about a student who can finally do research for school. When you pay for a snack with an app, imagine the farmers in Africa who can safely and instantly receive payments from buyers. If you email your resume to a new company, picture women applying for jobs and entering the workforce for the very first time. A connected life is a safe, happy, and informed life full of potential.
Now is the time to bring mobile connectivity to the rest of the world. When people are connected, their lives and the lives of those around them can be positively transformed. The KaiOS light operating system runs on affordable smart feature phones, which makes mobile internet more accessible to people in developing areas. If you would like to learn more about KaiOS’s mission to close the digital divide, or interested in launching a device or an app that runs on our platform, please contact us at partnership@kaiostech.com.